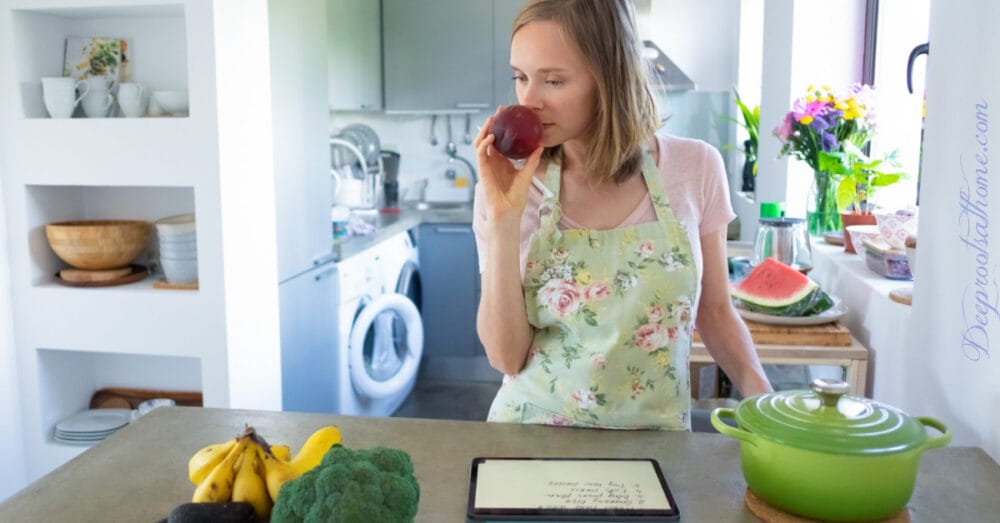

While we’ve been led to believe loss of taste and smell is a unique symptom of one particular “virus” (and can be a prolonged long-hauler symptom), in actuality, there are lots of other disorders that can cause loss of taste or smell.
The Root Causes Are Many
Nasal congestion, aging, hormonal changes, head or traumatic brain injuries, chemicals, smoking and street drugs, are a few of them. Also medical treatments and medications (side-effects): (source)
- Cancer treatment, particularly radiation to the head or neck
- Surgeries to the ears, nose or throat
Numerous drugs can affect both taste and smell (source):
- Antibiotics: amoxicillin, azithromycin and ciprofloxacin
- Blood pressure medication: amlodipine and enalapril
- Statin drugs: (lower cholesterol): atorvastatin, lovastatin and pravastatin
- Thyroid medication: levothyroxine
Drugs reported to affect taste only (source):
- Pain relievers: aspirin, ibuprofen and acetaminophen
- Blood pressure medications: furosemide, lisinopril, propranolol, hydrochlorothiazide and triamterene
But when it IS from the pesky “virus”, the loss of taste and smell is often the first sign. Not being able to smell or taste your food can be an upsetting realization, but this doesn’t typically last long, and you can help decrease these symptoms from home.
Although taste and smell are two distinct senses, they’re closely intertwined. Most people who think they’ve lost taste have actually just lost smell. That’s because smell contributes so much to taste that when the olfactory cells aren’t working properly, you have a hard time tasting food. (source)
How does the sense of smell work?
Food or other molecules in the air activate your sense of smell. These molecules enter your nose and mouth and attach to receptor cells in nasal mucus membranes. All those receptors then send that information they’ve gathered to the central nervous system, and your brain interprets it.
4 Ways To Help Get Back Smell and Taste
Homeopathy:
There are several homeopathic remedies that are known to make a quick job of it.
In this post, Joette Calabrese, HMC, CCH, PHom M, recommends Sanguinaria 200, twice daily, as a first-line remedy for the loss of smell and taste. For many, this may be the quick and easy answer, plus the Sanguinaria can clear sinuses to pre-sickness perfection.
She then writes,
“However, it may not be a perfect fit for your experience. I’ve had it work beautifully for some clients, yet I’m aware of others who saw no improvement with Sanguinaria.
“In homeopathy, there is more than one way to skin a cat. If after several days or so of Sanguinaria with no improvement, Sulphur 30 (also used twice daily) is another good choice. I especially lean toward Sulphur if the sufferer has had the cold or sinus infection for an extended time.
“But let’s say Sulphur doesn’t fit well with your symptoms either.
“For those with whom Sanguinaria and Sulphur haven’t provided improvement, I discussed Colchicum 30, twice daily, in a recent Facebook Live entitled Phantom Smells. (Start at timestamp 10:00; end at 21:00).
“Colchicum is especially beneficial for a distorted sense of smell (where certain foods smell metallic, rotten or even smell like something else entirely). I’ve received several happy messages stating it’s worked well for those who didn’t respond to Sanguinaria.”
Chiropractic:
Dr. Kevin Ross claims to have cracked a code to bring back your taste and smell if you lost them after getting COVID-19. The Tempe chiropractor studied allergies for years and says this quick trick is something that has helped many.
A very interesting 2 minutes.
Smell Retraining Therapy:
The idea is simple: Treat the cells that sense odors like a muscle group, and “exercise” them every day. You take a set of 10 to 15 very strong smells that you would easily recognize (like coffee, eucalyptus, oranges, or chocolate) and deeply inhale them for 20 seconds, twice a day, for 3 months or longer. While this sounds strange, it has been shown in studies like this one from JAMA Insights to improve smell in people who have lost it for months or even years.
Many videos of people trying to trigger their sense of taste with aromatic foods like blackening oranges and eating them or biting into onions like they’re apples have made their way online. Some of these actually work. Olfactory training utilizes the body’s neuroplasticity, which is the body’s ability to form new neural pathways to recover the sense of smell.
Zinc:
Taste buds need zinc to function normally. While zinc deficiency is uncommon in the U.S., research shows that zinc supplements can help people with taste issues. Since some medications can cause a zinc deficiency too, let your doctor know about your loss of taste in case it might be a drug side-effect.
Please share what helped you regain your taste or smell in comments!
“O taste and see that the Lord is good; How blessed is the man who takes refuge in Him!” ~Psalm 34:8
***For the Full Spike Protein Protocol (including NAC) to protect from transmission from the “V” and to help those who took the “V”, go here.
Deep Roots At Home now has a PODCAST! We are covering everything from vaccines, parenting topics, alternative medicine. Head over today and like, share and download a few episodes! https://buff.ly/3KmTZZd
I’m still on FB but shadow-banned hard… If you want to stay connected, here is one way…
You can also find me on Instagram, MeWe and Telegram.
And please join me for my FREE newsletter. Click here.

©2024 Deep Roots at Home • All Rights Reserved















Related